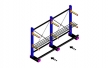
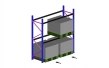
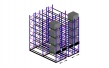
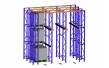
Low Voltage Switchboards
คำแนะนำ
An electric switchboard is a device that directs electricity from one or more sources of supply to several smaller regions of usage. It is an assembly of one or more panels, each of which contains switches that allow electricity to be redirected. The U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) defines a switchboard as "a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face, back, or both, switches, over-current and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments". The role of a switchboard is to allow the division of the current supplied to the switchboard into smaller currents for further distribution and to provide switching, current protection and (possibly) metering for those various currents. In general, switchboards may distribute power to transformers, panelboards, control equipment, and, ultimately, to individual system loads.
Inside a switchboard there will be one or more busbars. These are flat strips of copper or aluminum, to which the switchgear is connected. Busbars carry largecurrents through the switchboard, and are supported by insulators. Bare busbars are common, but many types are now manufactured with an insulating cover on the bars, leaving only connection points exposed.
The operator is protected from electrocution by safety switches and fuses. There may also be controls for the supply of electricity to the switchboard, coming from a generator or bank of electrical generators, especially frequency control of AC power and load sharing controls, plus gauges showing frequency and perhaps asynchroscope. The amount of power going into a switchboard must always equal to the power going out to the loads.
Modern industrial switchboards are metal enclosed and of "dead front" construction; no energized parts are accessible when the covers and panels are closed. Previously, open switchboards were made with switches and other devices were mounted on panels made of slate, granite, or ebony asbestos board. The metal enclosure of the switchboard is bonded to earth ground for protection of personnel. Large switchboards may be free-standing floor-mounted enclosures with provision for incoming connections at either the top or bottom of the enclosure. A switchboard may have incoming bus bars or bus duct for the source connection, and also for large circuits fed from the board. A switchboard may include a metering or control compartment separated from the power distribution conductors.
Inside a switchboard there will be one or more busbars. These are flat strips of copper or aluminum, to which the switchgear is connected. Busbars carry largecurrents through the switchboard, and are supported by insulators. Bare busbars are common, but many types are now manufactured with an insulating cover on the bars, leaving only connection points exposed.
The operator is protected from electrocution by safety switches and fuses. There may also be controls for the supply of electricity to the switchboard, coming from a generator or bank of electrical generators, especially frequency control of AC power and load sharing controls, plus gauges showing frequency and perhaps asynchroscope. The amount of power going into a switchboard must always equal to the power going out to the loads.
Modern industrial switchboards are metal enclosed and of "dead front" construction; no energized parts are accessible when the covers and panels are closed. Previously, open switchboards were made with switches and other devices were mounted on panels made of slate, granite, or ebony asbestos board. The metal enclosure of the switchboard is bonded to earth ground for protection of personnel. Large switchboards may be free-standing floor-mounted enclosures with provision for incoming connections at either the top or bottom of the enclosure. A switchboard may have incoming bus bars or bus duct for the source connection, and also for large circuits fed from the board. A switchboard may include a metering or control compartment separated from the power distribution conductors.